|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
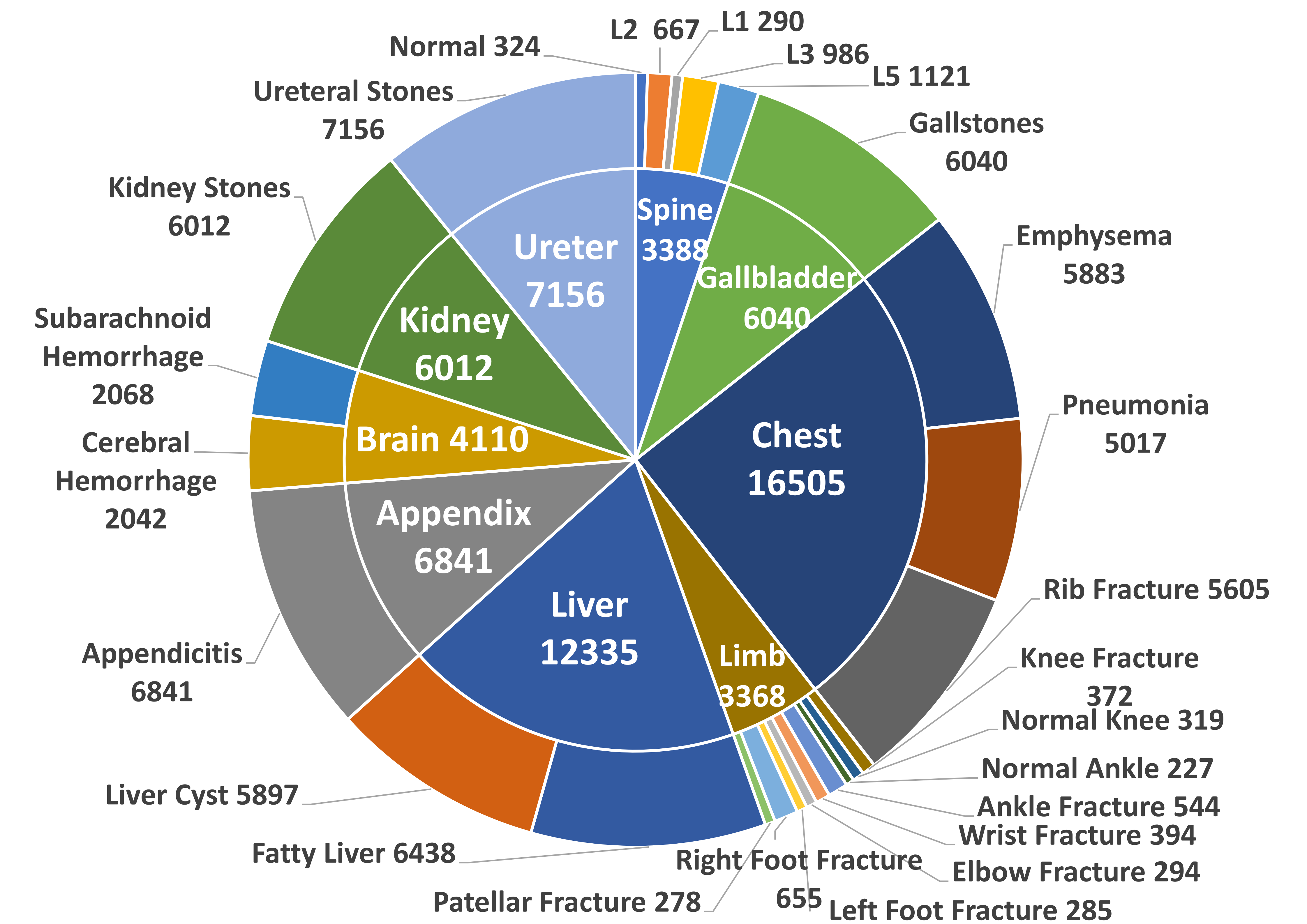
ACM MultiMedia 2025 Dataset
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
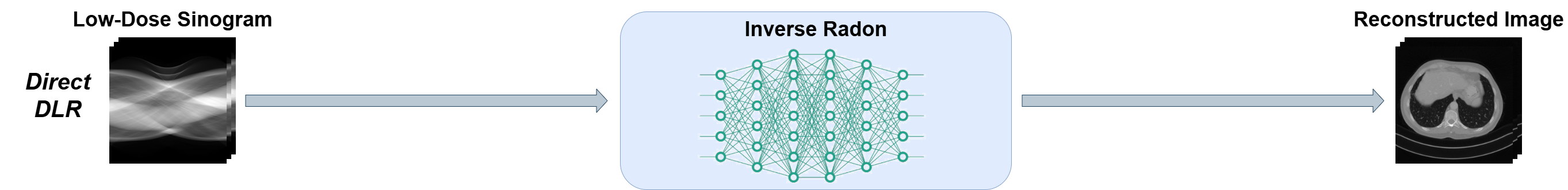
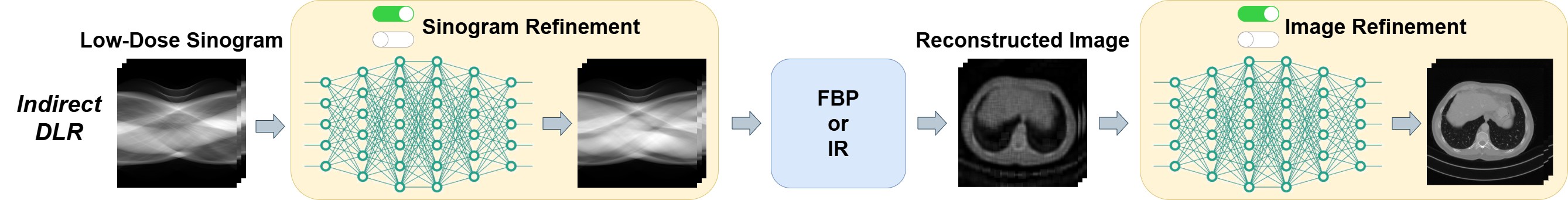
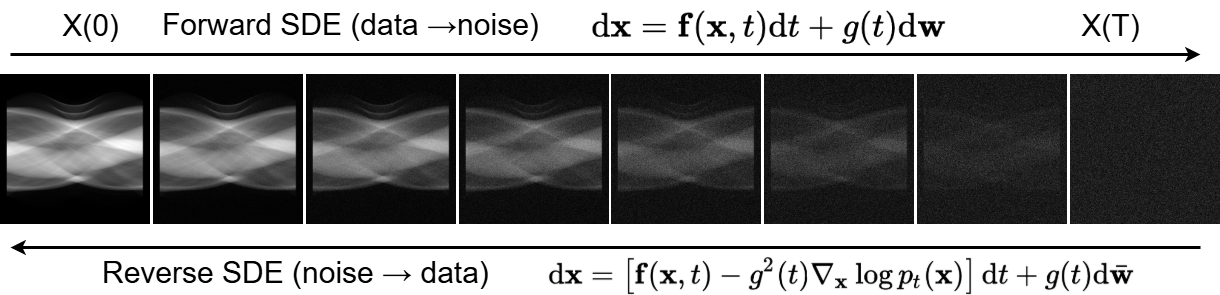
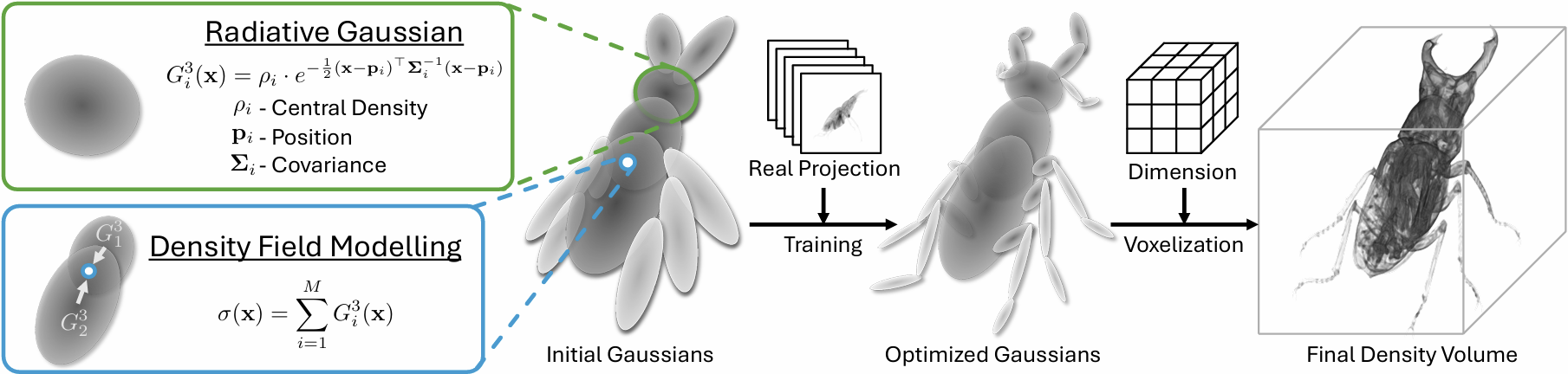
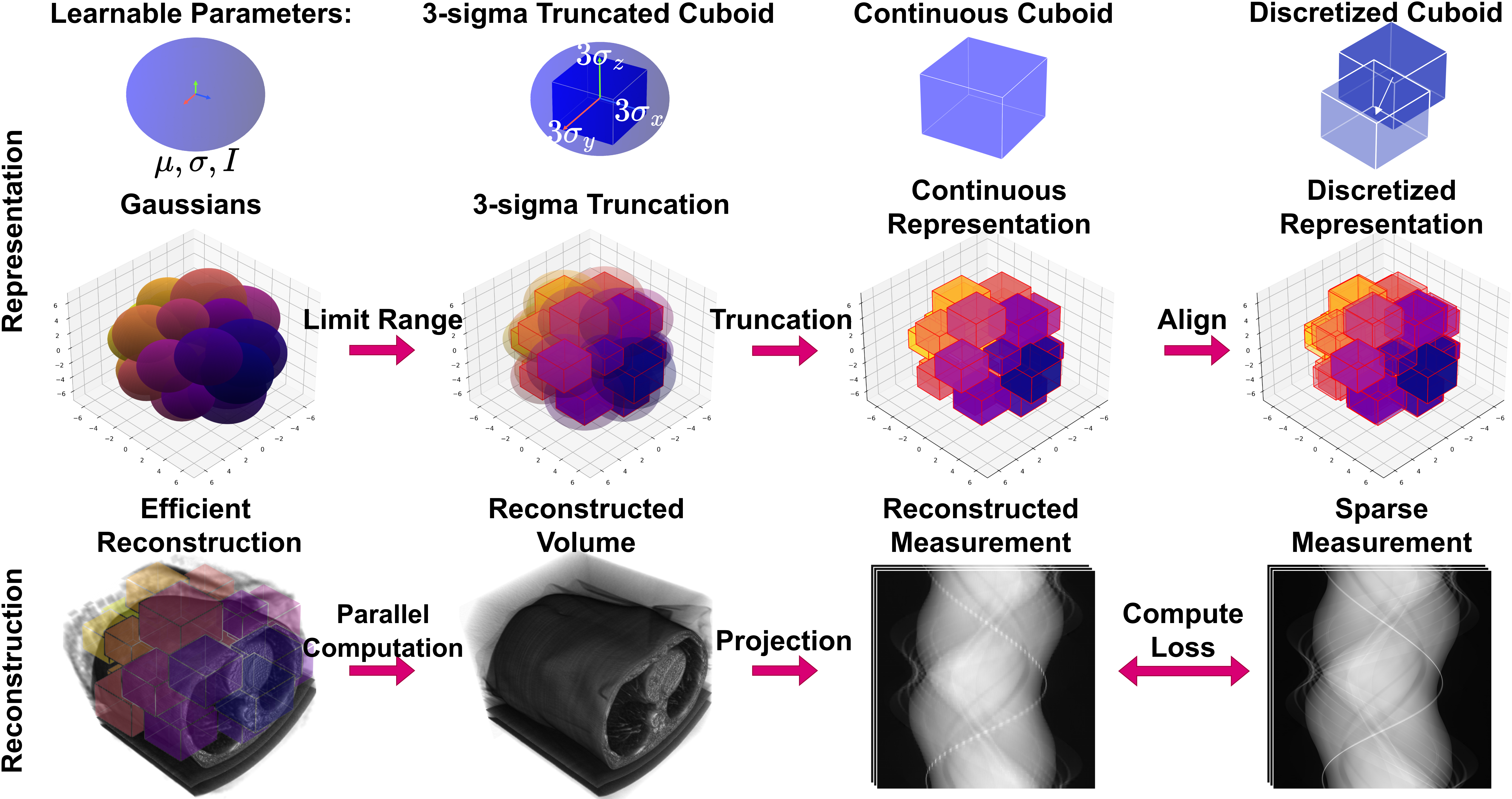
| Emphysema Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 29.58 | 0.714 | 28.44 | 0.644 | 27.06 | 0.623 | 27.27 | 0.588 |
| MCG | ✓ | 32.72 | 0.820 | 32.84 | 0.821 | 34.47 | 0.843 | 32.90 | 0.820 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 32.58 | 0.933 | 32.64 | 0.936 | 32.45 | 0.932 | 32.24 | 0.932 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 35.38 | 0.879 | 34.52 | 0.864 | 33.78 | 0.849 | 32.30 | 0.827 |
| FBP | × | 18.55 | 0.365 | 16.29 | 0.293 | 14.77 | 0.248 | 12.03 | 0.193 |
| NeRP | × | 25.41 | 0.744 | 25.21 | 0.735 | 25.40 | 0.745 | 25.39 | 0.745 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 38.88 | 0.943 | 38.52 | 0.939 | 37.95 | 0.932 | 37.69 | 0.928 |
| GIFT | × | 39.47 | 0.950 | 39.04 | 0.946 | 38.42 | 0.941 | 38.04 | 0.937 |
| Ureteral Calculi Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 37.04 | 0.901 | 35.63 | 0.913 | 32.07 | 0.759 | 31.46 | 0.844 |
| MCG | ✓ | 37.94 | 0.901 | 37.99 | 0.901 | 38.04 | 0.902 | 38.05 | 0.902 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 38.37 | 0.968 | 38.24 | 0.967 | 38.13 | 0.967 | 38.90 | 0.966 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 42.35 | 0.973 | 40.93 | 0.967 | 39.42 | 0.960 | 37.63 | 0.947 |
| FBP | × | 23.09 | 0.515 | 19.42 | 0.462 | 16.89 | 0.416 | 14.02 | 0.355 |
| NeRP | × | 26.91 | 0.801 | 26.68 | 0.789 | 26.95 | 0.802 | 26.66 | 0.785 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 41.37 | 0.971 | 41.09 | 0.966 | 40.05 | 0.962 | 39.45 | 0.956 |
| GIFT | × | 43.43 | 0.982 | 42.24 | 0.980 | 40.82 | 0.976 | 40.11 | 0.975 |
| Rib Fracture Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 29.61 | 0.707 | 28.97 | 0.682 | 27.94 | 0.658 | 27.97 | 0.585 |
| MCG | ✓ | 34.81 | 0.851 | 34.94 | 0.852 | 34.96 | 0.853 | 35.07 | 0.854 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 34.64 | 0.950 | 34.64 | 0.952 | 34.54 | 0,951 | 34.35 | 0.950 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 36.51 | 0.877 | 35.90 | 0.864 | 35.53 | 0.855 | 34.76 | 0.838 |
| FBP | × | 19.33 | 0.388 | 16.64 | 0.324 | 14.76 | 0.280 | 12.69 | 0.230 |
| NeRP | × | 25.77 | 0.778 | 25.10 | 0.744 | 25.63 | 0.771 | 25.60 | 0.769 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 40.72 | 0.960 | 39.48 | 0.952 | 38.65 | 0.948 | 37.68 | 0.943 |
| GIFT | × | 42.43 | 0.972 | 41.05 | 0.962 | 40.01 | 0.953 | 39.43 | 0.948 |
| Appendicitis Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 36.96 | 0.904 | 35.54 | 0.906 | 31.30 | 0.838 | 32.59 | 0.854 |
| MCG | ✓ | 38.76 | 0.908 | 38.96 | 0.909 | 38.97 | 0.897 | 38.36 | 0.899 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 38.34 | 0.960 | 38.28 | 0.959 | 38.24 | 0.966 | 38.00 | 0.967 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 44.18 | 0.976 | 42.62 | 0.971 | 40.85 | 0.964 | 37.79 | 0.949 |
| FBP | × | 23.37 | 0.516 | 19.63 | 0.462 | 18.17 | 0.427 | 14.67 | 0.366 |
| NeRP | × | 27.15 | 0.821 | 27.25 | 0.817 | 27.38 | 0.819 | 27.28 | 0.817 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 41.47 | 0.964 | 40.78 | 0.959 | 40.16 | 0.954 | 39.79 | 0.948 |
| GIFT | × | 42.03 | 0.981 | 41.63 | 0.981 | 41.15 | 0.979 | 40.22 | 0.976 |
| Pneumonia Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 31.78 | 0.733 | 30.43 | 0.672 | 29.22 | 0.680 | 27.82 | 0.578 |
| MCG | ✓ | 32.87 | 0.810 | 33.05 | 0.813 | 33.19 | 0.814 | 33.33 | 0.815 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 33.34 | 0.954 | 33.26 | 0.953 | 33.10 | 0.952 | 32.86 | 0.951 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 39.69 | 0.901 | 38.75 | 0.887 | 38.02 | 0.875 | 36.40 | 0.850 |
| FBP | × | 17.57 | 0.323 | 15.73 | 0.264 | 14.66 | 0.229 | 12.73 | 0.182 |
| NeRP | × | 25.52 | 0.694 | 26.16 | 0.733 | 25.93 | 0.722 | 25.64 | 0.701 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 39.73 | 0.953 | 38.96 | 0.949 | 38.40 | 0.944 | 37.92 | 0.938 |
| GIFT | × | 41.77 | 0.967 | 40.96 | 0.962 | 40.31 | 0.956 | 39.11 | 0.946 |
| Cerebral Hemorrhage Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 35.47 | 0.895 | 33.29 | 0.864 | 30.46 | 0.786 | 29.26 | 0.766 |
| MCG | ✓ | 39.14 | 0.898 | 39.23 | 0.899 | 39.32 | 0.899 | 39.31 | 0.899 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 39.04 | 0.969 | 39.29 | 0.973 | 39.05 | 0.971 | 38.53 | 0.969 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 34.90 | 0.742 | 33.50 | 0.740 | 31.86 | 0.737 | 29.57 | 0.732 |
| FBP | × | 24.13 | 0.526 | 21.54 | 0.490 | 19.70 | 0.460 | 17.52 | 0.413 |
| NeRP | × | 25.38 | 0.789 | 25.98 | 0.804 | 25.02 | 0.760 | 24.23 | 0.764 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 40.97 | 0.968 | 40.54 | 0.964 | 39.88 | 0.960 | 38.79 | 0.955 |
| GIFT | × | 43.71 | 0.984 | 42.94 | 0.981 | 41.68 | 0.978 | 40.56 | 0.974 |
| Kidney Stones Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 36.65 | 0.882 | 34.70 | 0.909 | 31.98 | 0.802 | 30.89 | 0.798 |
| MCG | ✓ | 38.16 | 0.909 | 38.43 | 0.911 | 38.49 | 0.912 | 38.67 | 0.913 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 28.84 | 0.964 | 38.92 | 0.966 | 38.79 | 0.964 | 38.54 | 0.964 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 43.58 | 0.980 | 42.27 | 0.976 | 40.95 | 0.971 | 39.51 | 0.961 |
| FBP | × | 22.88 | 0.483 | 19.39 | 0.439 | 16.27 | 0.398 | 13.52 | 0.341 |
| NeRP | × | 26.17 | 0.767 | 26.25 | 0.773 | 26.11 | 0.772 | 26.16 | 0.776 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 44.00 | 0.983 | 42.94 | 0.978 | 41.97 | 0.975 | 40.26 | 0.969 |
| GIFT | × | 44.37 | 0.988 | 43.45 | 0.987 | 42.99 | 0.986 | 41.20 | 0.982 |
| Fatty Liver Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 36.60 | 0.857 | 35.64 | 0.876 | 32.48 | 0.743 | 32.73 | 0.836 |
| MCG | ✓ | 37.97 | 0.897 | 38.07 | 0.897 | 38.12 | 0.898 | 38.14 | 0.898 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 38.04 | 0.961 | 37.95 | 0.960 | 37.86 | 0.960 | 37.68 | 0.959 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 43.47 | 0.973 | 42.21 | 0.968 | 40.76 | 0.961 | 38.45 | 0.948 |
| FBP | × | 22.29 | 0.482 | 18.10 | 0.431 | 16.54 | 0.395 | 13.87 | 0.342 |
| NeRP | × | 26.89 | 0.785 | 27.27 | 0.808 | 26.81 | 0.784 | 26.93 | 0.792 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 42.58 | 0.977 | 42.03 | 0.974 | 41.36 | 0.969 | 40.80 | 0.965 |
| GIFT | × | 44.46 | 0.987 | 43.96 | 0.986 | 43.47 | 0.985 | 42.54 | 0.983 |
| Gallbladder Stones Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 36.15 | 0.892 | 35.59 | 0.913 | 32.41 | 0.797 | 31.80 | 0.868 |
| MCG | ✓ | 38.13 | 0.897 | 38.47 | 0.901 | 38.01 | 0.897 | 37.95 | 0.899 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 38.20 | 0.966 | 38.22 | 0.966 | 38.19 | 0.967 | 37.86 | 0.965 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 43.66 | 0.974 | 42.34 | 0.969 | 40.56 | 0.961 | 37.64 | 0.943 |
| FBP | × | 23.94 | 0.548 | 20.27 | 0.494 | 17.46 | 0.445 | 14.68 | 0.380 |
| NeRP | × | 27.03 | 0.809 | 27.12 | 0.814 | 26.81 | 0.799 | 26.86 | 0.806 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 42.58 | 0.982 | 41.93 | 0.979 | 41.56 | 0.975 | 41.03 | 0.972 |
| GIFT | × | 43.73 | 0.985 | 42.91 | 0.984 | 42.15 | 0.982 | 40.55 | 0.977 |
| Hepatic Cyst Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 36.74 | 0.930 | 35.52 | 0.905 | 31.33 | 0.791 | 33.36 | 0.854 |
| MCG | ✓ | 37.87 | 0.891 | 37.91 | 0.891 | 37.94 | 0.891 | 37.94 | 0.891 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 37.92 | 0.955 | 38.02 | 0.957 | 37.91 | 0.956 | 37.50 | 0.952 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 42.84 | 0.973 | 41.42 | 0.967 | 39.81 | 0.960 | 37.12 | 0.946 |
| FBP | × | 25.26 | 0.603 | 19.94 | 0.525 | 17.27 | 0.475 | 14.26 | 0.416 |
| NeRP | × | 26.65 | 0.808 | 26.57 | 0.804 | 26.65 | 0.808 | 26.39 | 0.799 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 42.05 | 0.976 | 41.57 | 0.972 | 40.83 | 0.967 | 40.02 | 0.966 |
| GIFT | × | 42.96 | 0.981 | 42.29 | 0.980 | 41.47 | 0.977 | 39.12 | 0.971 |
| Elbow Fracture Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 34.41 | 0.847 | 34.05 | 0.789 | 27.42 | 0.777 | 29.82 | 0.732 |
| MCG | ✓ | 37.20 | 0.857 | 37.13 | 0.858 | 37.08 | 0.856 | 36.80 | 0.852 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 37.06 | 0.932 | 36.93 | 0.930 | 36.89 | 0.931 | 36.75 | 0.930 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 42.83 | 0.959 | 38.67 | 0.917 | 37.39 | 0.901 | 34.71 | 0.865 |
| FBP | × | 26.15 | 0.459 | 22.32 | 0.382 | 19.93 | 0.337 | 16.95 | 0.279 |
| NeRP | × | 28.14 | 0.826 | 28.31 | 0.827 | 28.06 | 0.823 | 28.18 | 0.835 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 41.99 | 0.950 | 41.37 | 0.946 | 40.63 | 0.942 | 40.12 | 0.939 |
| GIFT | × | 42.82 | 0.961 | 41.94 | 0.954 | 41.19 | 0.949 | 39.97 | 0.948 |
| Spinal Fracture Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 23.86 | 0.866 | 23.94 | 0.841 | 23.92 | 0.832 | 23.70 | 0.810 |
| MCG | ✓ | 38.52 | 0.913 | 38.52 | 0.913 | 38.48 | 0.912 | 38.40 | 0.911 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 39.34 | 0.973 | 39.27 | 0.973 | 39.08 | 0.972 | 38.49 | 0.969 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 40.94 | 0.946 | 38.02 | 0.930 | 34.68 | 0.901 | 28.85 | 0.834 |
| FBP | × | 16.41 | 0.793 | 15.20 | 0.766 | 14.73 | 0.741 | 13.96 | 0.698 |
| NeRP | × | 28.10 | 0.847 | 26.24 | 0.779 | 27.95 | 0.840 | 26.48 | 0.790 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 40.51 | 0.970 | 39.06 | 0.961 | 38.33 | 0.957 | 37.98 | 0.953 |
| GIFT | × | 41.23 | 0.981 | 39.70 | 0.977 | 38.41 | 0.971 | 37.68 | 0.968 |
| Foot Fracture Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 37.53 | 0.860 | 35.61 | 0.783 | 32.52 | 0.817 | 32.46 | 0.837 |
| MCG | ✓ | 39.40 | 0.891 | 39.62 | 0.895 | 39.43 | 0.894 | 39.45 | 0.894 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 40.45 | 0.956 | 40.31 | 0.955 | 40.22 | 0.954 | 40.26 | 0.957 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 34.92 | 0.927 | 36.40 | 0.905 | 31.95 | 0.866 | 28.33 | 0.783 |
| FBP | × | 23.45 | 0.235 | 18.80 | 0.181 | 17.23 | 0.160 | 14.46 | 0.132 |
| NeRP | × | 30.69 | 0.921 | 30.82 | 0.926 | 30.76 | 0.932 | 30.56 | 0.927 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 39.97 | 0.960 | 39.12 | 0.956 | 38.46 | 0.951 | 37.90 | 0.949 |
| GIFT | × | 41.81 | 0.981 | 41.21 | 0.980 | 40.51 | 0.974 | 39.60 | 0.977 |
| Wrist Fracture Reconstruction | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 36.61 | 0.810 | 34.73 | 0.825 | 31.73 | 0.870 | 30.78 | 0.744 |
| MCG | ✓ | 37.14 | 0.887 | 37.53 | 0.889 | 37.65 | 0.890 | 37.64 | 0.889 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 36.91 | 0.953 | 36.94 | 0.954 | 36.73 | 0.952 | 36.31 | 0.950 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 36.74 | 0.903 | 33.91 | 0.874 | 31.57 | 0.832 | 28.91 | 0.766 |
| FBP | × | 21.35 | 0.231 | 17.95 | 0.197 | 15.69 | 0.174 | 12.96 | 0.146 |
| NeRP | × | 29.55 | 0.893 | 28.77 | 0.891 | 29.62 | 0.897 | 29.56 | 0.893 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 38.42 | 0.974 | 38.04 | 0.973 | 37.66 | 0.970 | 36.98 | 0.967 |
| GIFT | × | 40.28 | 0.984 | 39.71 | 0.983 | 38.89 | 0.976 | 37.78 | 0.973 |
| Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Pretrain | 180-view | 120-view | 90-view | 60-view | ||||
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| RED-CNN | ✓ | 29.52 | 0.874 | 29.65 | 0.877 | 29.55 | 0.877 | 29.42 | 0.863 |
| MCG | ✓ | 38.78 | 0.908 | 38.87 | 0.909 | 38.81 | 0.908 | 38.79 | 0.908 |
| DiffusionMBIR | ✓ | 39.46 | 0.975 | 39.38 | 0.975 | 39.20 | 0.974 | 38.70 | 0.973 |
| SWORD | ✓ | 42.54 | 0.965 | 39.60 | 0.955 | 36.71 | 0.938 | 31.84 | 0.895 |
| FBP | × | 21.31 | 0.440 | 20.84 | 0.423 | 19.22 | 0.404 | 17.93 | 0.361 |
| NeRP | × | 23.72 | 0.760 | 23.34 | 0.760 | 23.84 | 0.800 | 24.04 | 0.791 |
| R2-Gaussian | × | 41.89 | 0.973 | 41.11 | 0.968 | 40.35 | 0.964 | 39.77 | 0.956 |
| GIFT | × | 43.29 | 0.993 | 42.74 | 0.993 | 41.98 | 0.992 | 41.02 | 0.992 |